Last Updated on 09 Jul 2025
OSTA: Odoo Security Threat Analyzer, Scan, Detect, and Defend Your ERP
Share in

Introduction to Odoo
Odoo by the Numbers (2024)
•
🌍 12+ million users worldwide•
🗺️ Used in over 120 countries•
🏢 3,200+ official implementation partners•
🧩 39,000+ apps available on the Odoo App Store•
📦 Tens of thousands of production deployments globally•
🧑💻 Available in multiple hosting models: SaaS, Odoo.sh (PaaS), and On-Premise
These statistics demonstrate the scale, maturity, and trust Odoo has built within the global ERP ecosystem.
Notable Companies Using Odoo
•
Toyota – for automating internal workflows and dealer management•
Hyundai – for inventory and parts supply chain management•
Danone – for manufacturing and logistics operations•
WWF (World Wildlife Fund) – for donor and program management•
Harvard University – for academic and research department support•
The State of Michigan – for public sector administrative functions
•
Odoo Customer Success Stories

Deployment Options: On-Premise vs Odoo Online vs Odoo.sh
| Deployment Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Odoo Online (SaaS) | Quick setup, fully managed by Odoo, automatic updates, no server maintenance needed | Limited customization, cannot install third-party modules, limited root access |
| Odoo.sh (PaaS) | Managed hosting with more flexibility, supports custom modules, integrated CI/CD | More technical knowledge required, slightly higher cost, still some limitations in root access |
| On-Premise (Self-Hosted) | Full control, deep customization, access to all modules and databases | Requires in-house technical expertise, responsible for security, backups, and updates |
While Odoo Online is ideal for fast, plug-and-play adoption, companies with complex processes often choose Odoo.sh or On-Premise setups to meet custom needs and integration requirements. However, as deployment flexibility increases, so does the security responsibility, which is often underestimated.
Odoo Security Concerns
•
The Rising Threat LandscapeAccording to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023, the global average cost of a data breach has reached $4.45 million, marking a 15% increase over three years. Meanwhile, over 30,000 websites are hacked every day (Forbes, 2023), with small and mid-sized businesses, like those often using Odoo, becoming increasingly popular targets due to less robust security postures.But the game is changing yet again. With the emergence of agentic AI systems, the threat landscape is evolving from reactive automation to proactive, autonomous agents capable of crafting, iterating, and launching attacks at scale. Unlike traditional bots, agentic AI doesn’t just execute—it plans, adapts, and learns. As discussed in CrossClassify’s recent post, "Agentic AI Is Coming", this new generation of AI brings significant cybersecurity challenges, particularly for open-source platforms like Odoo that can be probed and exploited in creative ways.This convergence of increasing attack sophistication, emerging AI threats, and widespread adoption of business-critical platforms like Odoo demands a more serious and proactive approach to log monitoring, anomaly detection, user behavior modeling, and layered defense mechanisms. A strong strategy begins by understanding the specific vulnerabilities and real-world threats that have already surfaced.•
Real Security Incidents and Vulnerabilities in OdooOdoo, while powerful and widely adopted, has not been immune to security issues. A series of critical vulnerabilities and public disclosures illustrate just how vital it is to secure and monitor your Odoo instance:•
Critical Broken Access Control in Odoo 14.0A real-world exploitation case detailed here reveals how unauthenticated users could gain unauthorized access to sensitive information and manipulate documents. The flaw stemmed from poor access control implementations—an issue that could be mitigated with real-time log monitoring and behavioral anomaly detection.•
CVE-2021-23166This vulnerability affects the Odoo Web framework and allows cross-site scripting (XSS) via crafted SVG files. Full details available at OpenCVE.•
CVE-2021-45111This bug exposes internal server error messages through improper exception handling, potentially leaking system-level information. See more on OpenCVE.•
CVE-2021-45071An issue within the web client that could allow injection of malicious content due to insecure parsing of HTTP requests. Technical details are available here.•
Data Exposure in Shared DatabasesAs highlighted by Maherban Ali on LinkedIn, instances of shared database environments (especially in SaaS deployments) pose risks of accidental data exposure or insufficient tenant isolation.
According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023, the global average cost of a data breach has surged to $4.45 million, a 15% increase over the past three years. Meanwhile, Verizon’s 2024 DBIR reports that 74% of breaches involve the human element, including social engineering, privilege misuse, and errors. Odoo, like any ERP system, is not immune to these risks.What makes today’s environment even more complex is the emergence of agentic and generative AI tools. Threat actors now have access to intelligent bots capable of launching sophisticated phishing campaigns, scanning vulnerabilities at scale, and crafting highly personalized attacks. These AI-driven threats elevate the playing field—making traditional security measures insufficient in isolation.As outlined in our article on Odoo Security Best Practices, securing an Odoo deployment requires a holistic approach that spans technical configurations, human behavior, and system architecture. It’s not just about patching software; it’s about reinforcing every layer of the ecosystem.•
The Shared Responsibility of Odoo SecuritySecurity in Odoo—like in most enterprise platforms—is a shared responsibility. Much like a chain, the overall security posture is only as strong as its weakest link. Ensuring robust protection requires vigilance and alignment across all key actors:
1.
The Odoo Product OwnerThis stakeholder is responsible for choosing the deployment model—on-premise, Odoo.sh, or Odoo Online. Each option brings a distinct set of security implications:•
On-premise deployments give full control but also place the full burden of protection (updates, firewalling, backups, access logs) on the organization.•
Odoo.sh provides managed hosting with CI/CD integrations, but still requires thoughtful configuration and security best practices.•
Odoo Online, while easiest to manage, limits customization and visibility—making it less suitable for regulated industries or those with complex security needs.
The deployment decision fundamentally affects what types of black-box or white-box scanning and protection mechanisms are appropriate.2.
The Odoo Admin UserOnce Odoo is deployed, admin users configure roles, permissions, and data access policies. This step is often underestimated, but a single misconfigured access control can open the door to role-based attacks or data leakage. Admins must:•
Set up role-based access control (RBAC) properly•
Regularly audit user groups and permissions•
Monitor and log critical actions
Failure to do so can create silent vulnerabilities that are hard to detect—but easy to exploit.3.
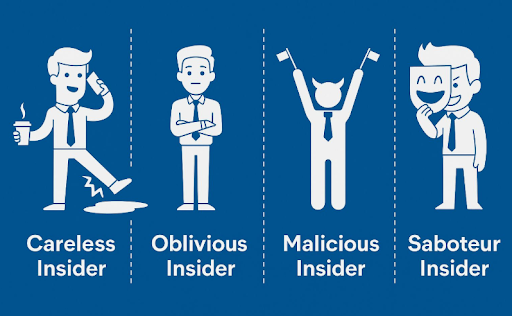
The Odoo End UsersEnd users interact with various modules of the Odoo platform—CRM, Sales, HR, etc.—based on permissions. While most users act in good faith, insider threats are an ever-present risk. Sometimes it’s intentional (data exfiltration); other times, it’s an unintentional misstep—like uploading sensitive documents without encryption or exposing internal notes to external parties.As explored in this LinkedIn post by Hossein Rah, insider threats are increasingly subtle and often bypass traditional security controls. The combination of behavioral analytics and real-time monitoring—such as what CrossClassify provides—becomes crucial in detecting and mitigating these risks.Odoo’s modularity and flexibility are what make it powerful, but they also make it vulnerable. Addressing security concerns across all three layers—the platform, the configuration, and the user behavior—is critical for resilient operations. With generative AI reshaping the threat landscape, security cannot remain static or siloed. It must evolve—continuously and collaboratively.That’s why tools like Odoo Security Scan—which combines black-box and white-box techniques—are built not only to detect vulnerabilities but to empower all stakeholders with actionable insights.
Varied Range of Threat Types
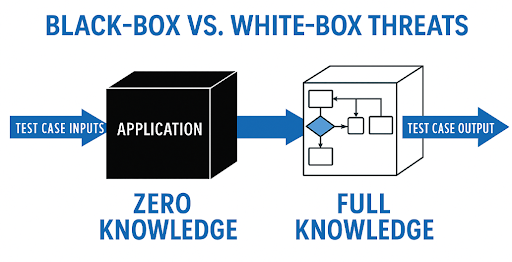
•
Odoo Product Owners: Decide on deployment strategy. On-premise deployments have different exposure risks compared to online deployments. Black-box threats like port scanning or brute force vary based on this deployment decision.•
Odoo Admin Users: Responsible for configuring users, roles, and permissions. Misconfigurations at this level can lead to role-based attacks or permission escalation vulnerabilities.•
Odoo End Users: Regular users interacting with the platform. If their accounts are compromised or misused, insider threats may emerge, either through intentional sabotage or accidental misuse.
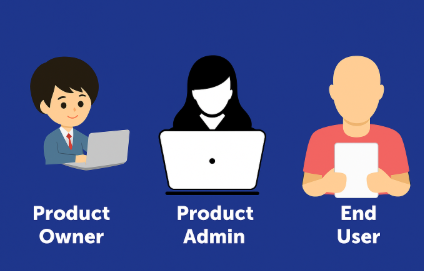
Specific Threat Types
1.
Credential Reuse Attacks using leaked credentials2.
Default Credential Stuffing testing commonly used credentials like "admin:admin" on exposed Odoo instances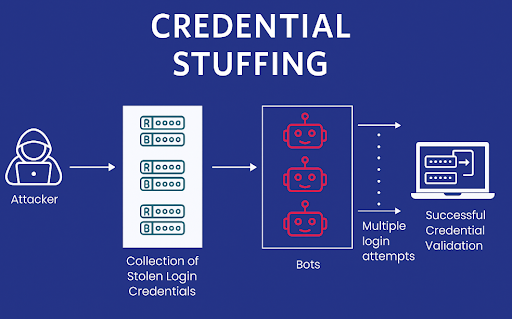


Users not belonging to any group may bypass group-based restrictions and gain unexpected access.
Non-admin users with admin-level privileges can perform unauthorized actions such as data export or user deletion.
Some groups may unintentionally replicate admin-level access, creating risk if any group member is compromised.
Groups with overlapping or redundant permissions can create ambiguity, complicating access control and audit.

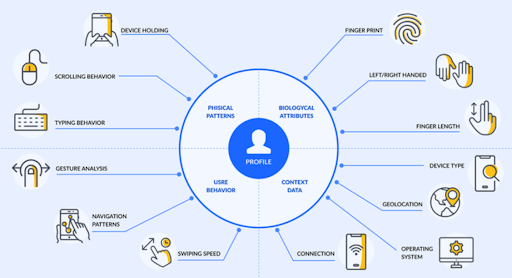
Anomalies in login or activity timing can reveal threats. For example, a user accessing Odoo at midnight rather than regular work hours may indicate compromise. "Impossible Travel" patterns—logins from geographically distant locations in short time—are a red flag.
If a user typically performs 10 actions a day but suddenly generates 200 requests, it may suggest automation or misuse.
A deviation in how users navigate—e.g., skipping normal flows and directly accessing sensitive panels—can indicate abuse or ATO.
APIs or admin routes left unprotected can be directly accessed by attackers.
Debug mode exposes internal stack traces and environment info. It should be disabled in production.
Weak encryption standards can be exploited for man-in-the-middle attacks.
Without secure and HttpOnly cookie flags, session tokens can be intercepted.
Headers like Content-Security-Policy and X-Frame-Options help harden browsers against XSS and clickjacking.
In some Odoo setups, the master password for database access is unset or uses weak defaults, creating critical risk.
Security Solutions
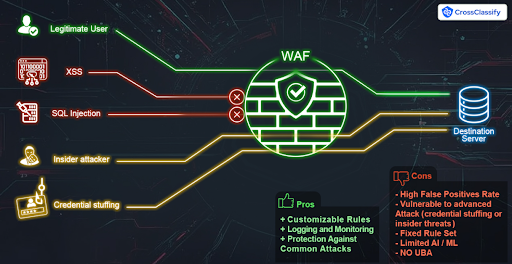


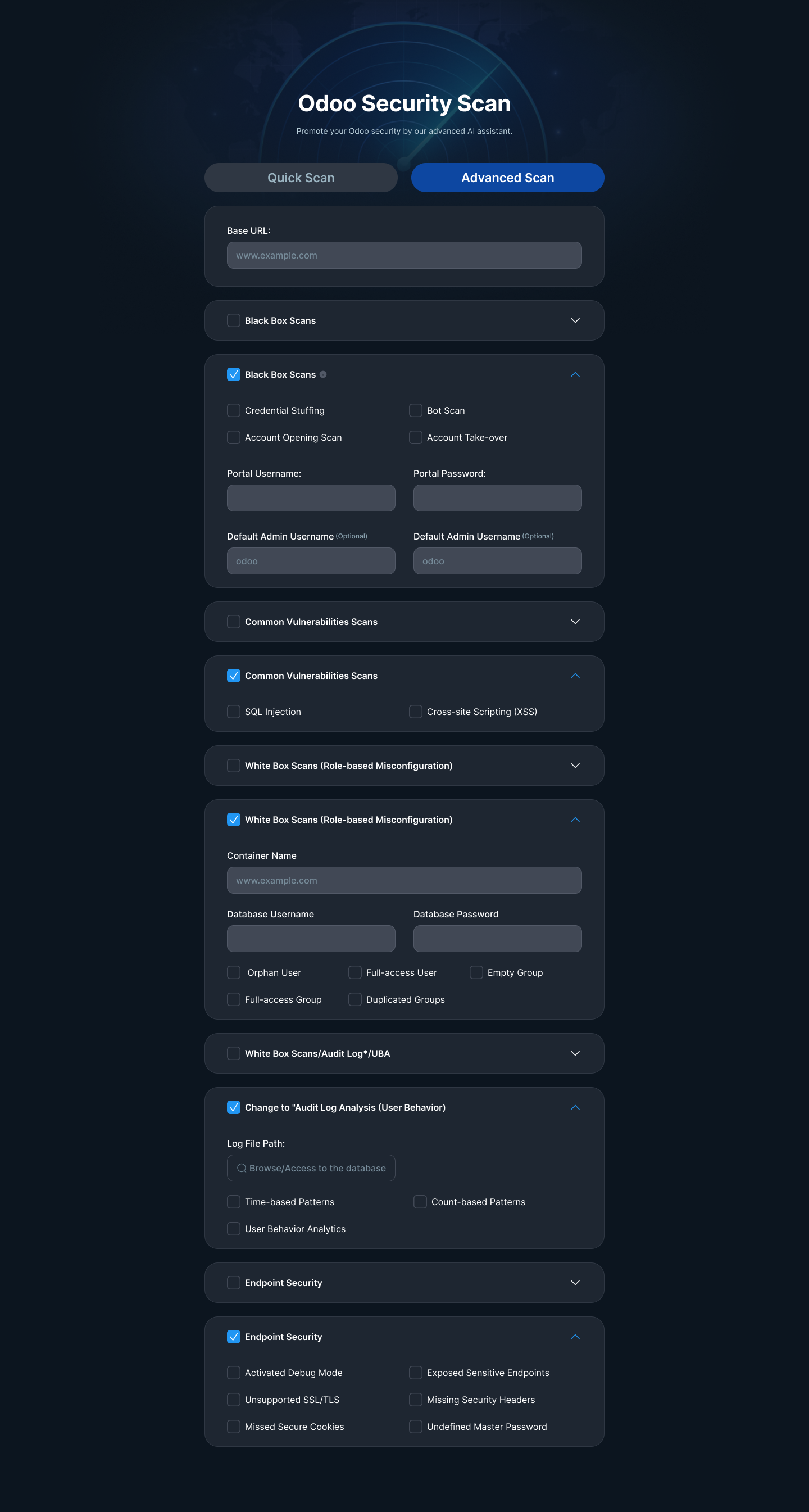
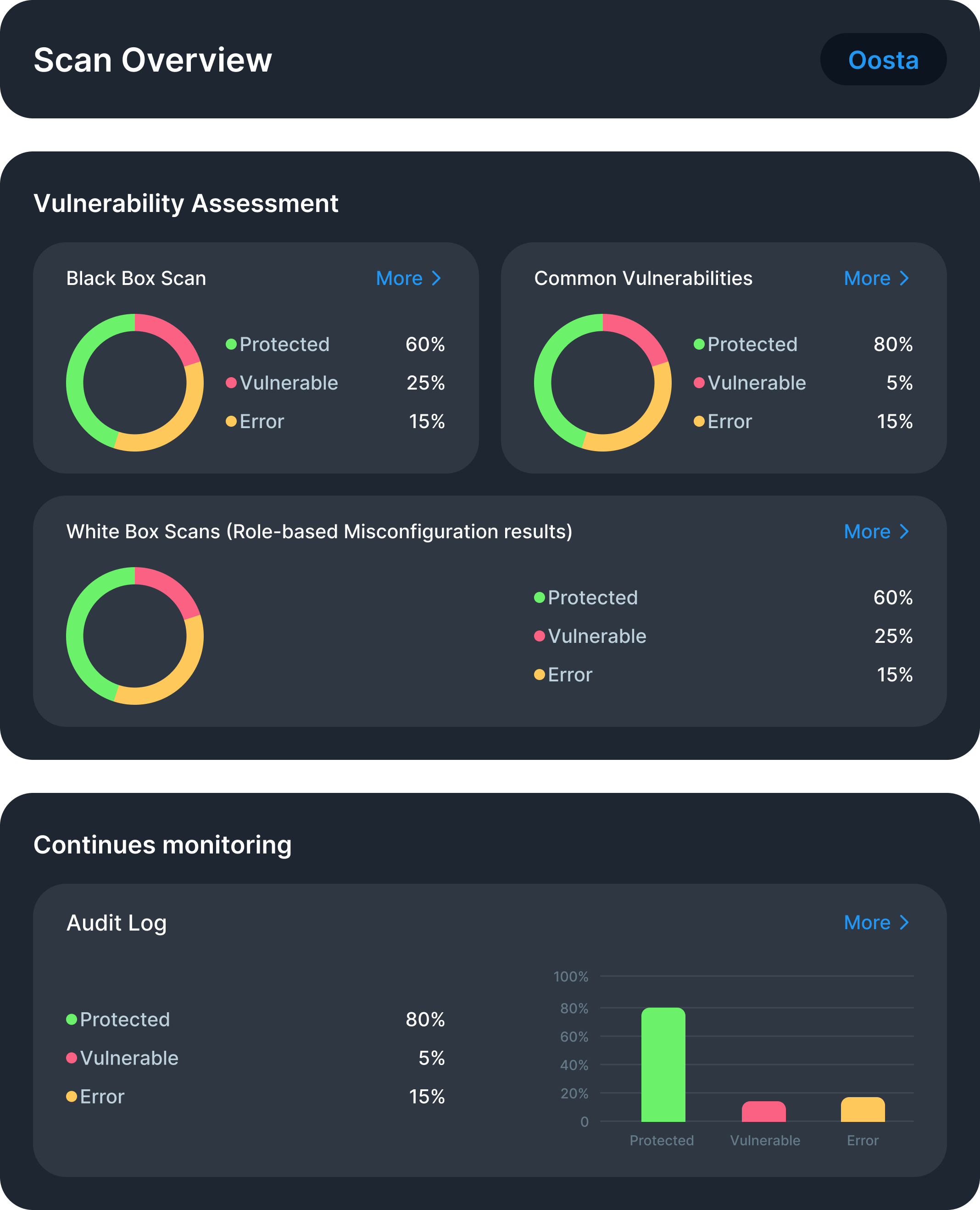
OSTA: Odoo Security Threat Analyzer

•
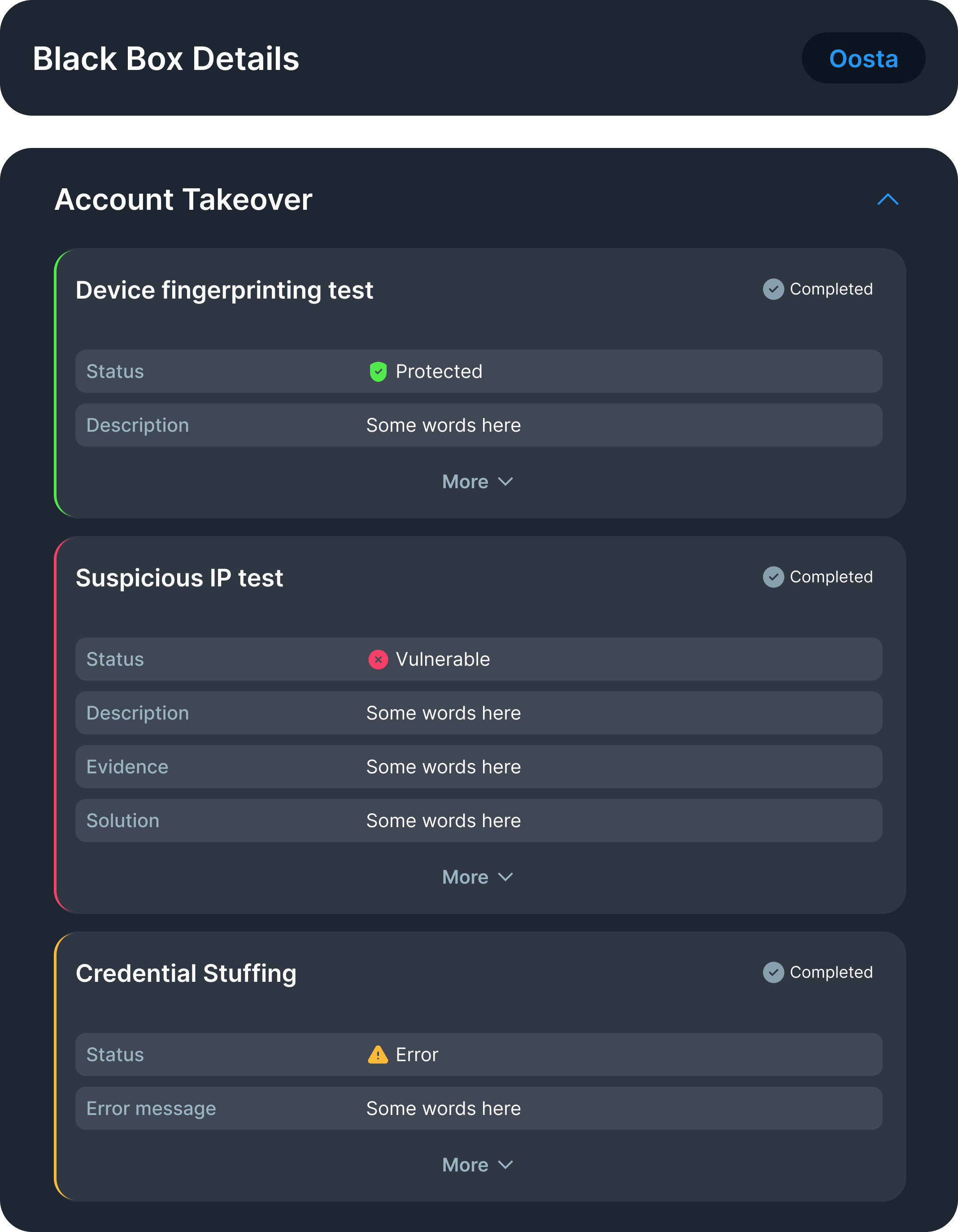
Protected: The system is secure against this threat.•
Vulnerable: A real threat exists and requires attention. Users can click "More" to see supporting evidence.•
Error: An issue occurred during testing (e.g., misconfigured endpoint or access denial).
•
Threat Detection: Covers black-box and white-box vulnerabilities•
Explainability: Delivers evidence and human-readable explanations•
Mitigation Guidance: Offers clear, actionable recommendations•
Continuous Monitoring: Empowers teams to move from reactive to adaptive security
See How Protecting Customers from the Growing Threat of Account Takeover
Ensure Continuous Security with Real-Time Account Monitoring

See How Protect Your Platform from Account Opening Fraud
CrossClassify uses AI and continuous behavior monitoring to detect and prevent Fake accounts, protecting your business processes

Explore CrossClassify today
Detect and prevent fraud in real time
Protect your accounts with AI-driven security
Try CrossClassify for FREE—3 months
Share in
Related articles
Frequently asked questions
- Credential stuffing
- SQL injection
- Cross-site scripting (XSS)
- Insider misuse
- Role-based misconfigurations
- Agentic AI-driven exploits
- Endpoint exposure and audit-log anomalies
- Simulates real-world threat behavior
- Provides human-readable explanations for each finding
- Offers tailored mitigation recommendations
- Supports both Quick Scan and Advanced Scan modes
- Includes behavioral threat detection powered by UBA (User Behavior Analysis)
Advanced Scan: Full-spectrum scan including white-box analysis (requires config/log access). Suitable for deep security audits and high-risk environments.
- Protected – No issues detected
- Vulnerable – Threat found with evidence
- Error – Scan failed due to access denial or misconfiguration
- Odoo Online (SaaS) – limited by access constraints
- Odoo.sh (PaaS) – deep scanning with CI/CD integration
- On-Premise – full control for maximum detection and remediation
Let's Get Started
Discover how to secure your app against fraud using CrossClassify
No credit card required



