Last Updated on 12 Aug 2025
Healthcare Cybersecurity and Fraud: A Deep Dive Into Today's Greatest Risks and Defenses
Share in

Key Notes
•
Healthcare fraud causes over $100 billion in annual losses in the U.S. alone.•
45 million individuals were affected by healthcare data breaches in 2021.•
34% of healthcare breaches involve internal actors.
Introduction to the Healthcare Industry
The healthcare industry has undergone a massive digital transformation over the past decade. With the widespread adoption of telemedicine, electronic health records (EHRs), and AI-driven diagnostics, patient care has become more accessible and efficient. However, this digitization has also expanded the attack surface for fraudsters and cybercriminals. Healthcare apps, patient portals, and connected medical devices are now entry points for threats that can compromise sensitive data and operations. As a result, cybersecurity is no longer optional, it's foundational for trust and continuity in care.

Market Size of the Healthcare Industry
The global healthcare market is valued at over $12 trillion as of 2024, with digital health projected to reach $660 billion by 2025. Over 70% of healthcare providers have implemented electronic health records globally, and telehealth visits surged by 154% in early 2020 alone. With over 195 countries and thousands of implementation partners across hospitals, insurers, and tech providers, the healthcare industry has become one of the largest and most interconnected sectors in the world. This scale not only increases efficiency but also raises security stakes exponentially.
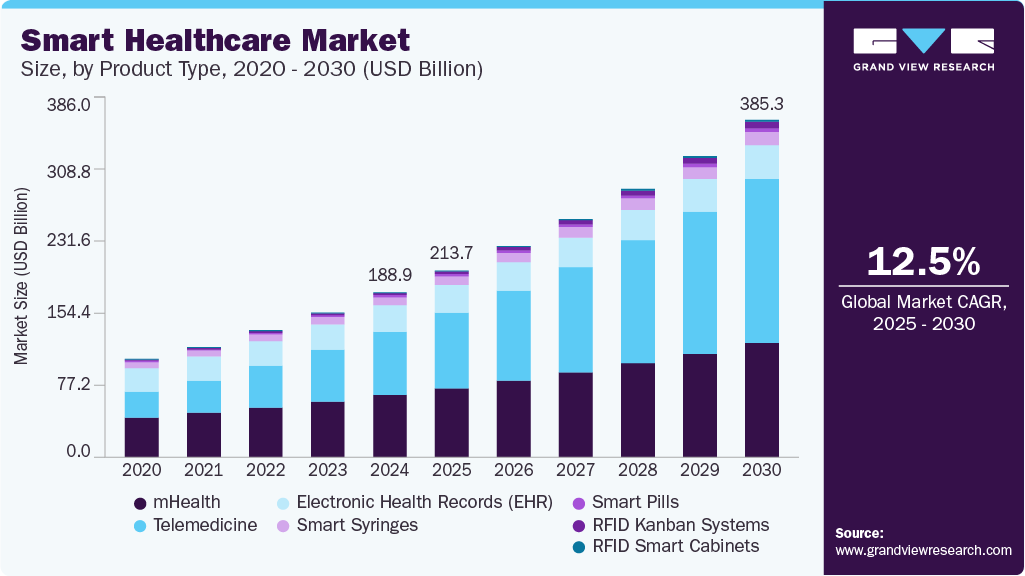
Fraud/Security Concerns: The Big Picture in Healthcare
Fraud and cybersecurity issues in healthcare fall into three primary categories:
•
Patient-Centric Threats: These include identity theft, unauthorized access to EHRs, and patient impersonation. Cybercriminals often sell patient records on the dark web, which can then be used for fake prescriptions or insurance claims.•
Provider-Centric Threats: Threat actors may manipulate claims, falsify services, or collude with fake vendors. Healthcare professionals or insiders can also abuse their access to confidential data for financial or personal gain.•
Infrastructure-Centric Threats: These include DDoS attacks on hospital portals, ransomware targeting lab systems, and API abuse in mobile apps. As healthcare adopts more IoT and cloud services, the risk landscape becomes more complex and harder to monitor.

Fraud Size in the Healthcare Industry
The National Health Care Anti-Fraud Association (NHCAA) estimates that healthcare fraud costs the U.S. over $100 billion annually. Globally, fraud accounts for approximately 6% of all healthcare spending. Cyberattacks on healthcare institutions have also increased by 74% year-over-year, highlighting a growing crisis that threatens both financial stability and patient safety. These figures underscore the urgent need for stronger fraud detection mechanisms.
Real-World Cases of Fraud in the Healthcare Industry
Healthcare fraud is not hypothetical. It occurs at all levels of the system:
•
Insider Threat at Mayo Clinic: A former employee accessed over 1,600 patient records without authorization. This breach highlighted the need for better internal monitoring.•
Fake Billing Schemes: The DOJ charged over 345 individuals in a $6 billion healthcare fraud and opioid abuse takedown in 2020. Source: DOJ Press Release•
Patient Identity Misuse: Hackers breached databases to create synthetic IDs and file false insurance claims, particularly targeting Medicaid and Medicare.
Insider Threats in Healthcare: The Hidden Risks Within
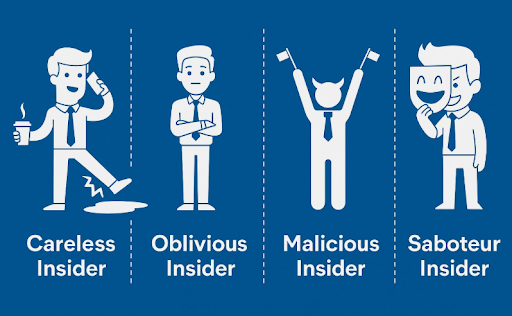
Insider threats in healthcare are not always malicious, but they are always dangerous. A significant number of breaches and fraud incidents originate from users with legitimate access. According to CrossClassify, there are four main types of insider threats:
•
Negligent or Unintentional Insiders: Employees who inadvertently click phishing links, misplace files, or send sensitive data to the wrong recipient. Their lack of awareness or training makes them the most common insider threat.•
Accidental Insiders: These are users who unknowingly create security holes, like misconfiguring access permissions or improperly storing patient data.•
Compromised Insiders: External attackers who hijack employee accounts via credential theft. These insiders appear legitimate but act maliciously on behalf of an attacker.•
Malicious Insiders: Individuals who deliberately leak, alter, or exploit patient data. They may do so for personal gain, revenge, or as part of collusion.
Insider threats are particularly hard to detect because they exploit trust and system familiarity. They highlight the need for behavior-based detection and real-time visibility.
Main Consequences of Not Being Protected Against Fraud and Data Breach
Failing to secure healthcare systems and digital infrastructures has far-reaching consequences that extend beyond financial penalties. The interconnected nature of healthcare delivery means that a breach or fraud event can ripple across departments, partners, and even entire health systems. Below are the key consequences healthcare organizations face if they lack adequate fraud protection and cybersecurity measures:
•
Financial Loss: Cyberattacks, fraud schemes, and regulatory fines can cost healthcare organizations millions of dollars. These costs may include direct theft, class action settlements, forensic investigations, ransomware payments, and system recovery. In some cases, fraudulently processed claims can drain insurance budgets, causing systemic financial strain.•
Reputation Damage: Patient trust is foundational to healthcare. A breach that exposes patient data or allows unauthorized access to medical records can irreparably damage a provider's reputation. Publicized incidents often lead to negative media coverage, social backlash, and decreased patient intake, especially in competitive urban markets.•
Patient Harm: Fraud and breaches can lead to incorrect medical information being recorded or shared. For instance, if a fraudster impersonates a patient to gain access to prescriptions, the real patient's records may be altered. This can result in misdiagnosis, improper treatment plans, or dangerous drug interactions, ultimately putting lives at risk.•
Legal Liabilities: Violations of data protection laws such as HIPAA, HITECH, and GDPR trigger legal consequences. These may include government-imposed penalties, audits, and lawsuits by affected patients. Non-compliance can also limit future funding opportunities and partnerships with public or private healthcare networks.•
Service Disruption: Cyberattacks like ransomware can bring operations to a halt. Hospitals may need to divert patients, reschedule surgeries, or operate offline, creating chaos and endangering lives. For digital-first platforms such as telemedicine providers, even a few hours of downtime can cause widespread disruption to care.
A stark example of the consequences is the EmblemHealth breach, where sensitive information of over 80,000 individuals was exposed due to a mailing error. Though seemingly minor, the breach resulted in massive fallout, highlighting that even small lapses in security protocols can trigger large-scale consequences.
Compliance Issues in the Healthcare Industry
Regulations like HIPAA (U.S.), HITECH, and GDPR (Europe) set strict mandates for healthcare data privacy and security. Yet compliance alone does not guarantee safety. Many organizations struggle with outdated infrastructure, shadow IT, and poor visibility into access controls. Breaches often reveal gaps in not just technology but also in policy enforcement and staff training. CrossClassify's solutions help healthcare providers go beyond compliance, building resilience through proactive monitoring and intelligent detection.

Fraud Types in the Healthcare Industry
•
Billing Fraud: Inflated, duplicated, or entirely fake claims filed for reimbursement. Providers may charge for services never rendered.•
Insider Threats: Employees or contractors misuse access for personal or financial gain. Insiders often know how to bypass controls, making detection harder. Learn more about insider threats•
Account Takeovers: Attackers gain control of patient or staff accounts through phishing, brute force, or credential stuffing. Once in, they can alter medical histories or approve fraudulent claims. Read about account takeover anatomy•
Synthetic IDs: Fraudsters combine real and fake data to create new identities. These are used to file fake claims or gain access to prescriptions.•
Medical Identity Theft: Criminals use stolen health data to receive care, often altering patient records in the process.•
Telemedicine Abuse: Fraudulent consultations or remote diagnoses billed without actual care provided.•
Fake Clinics & Pharmacies: Shell organizations that bill insurers for non-existent services.•
Bot Attacks on Portals: Automated scripts try to access patient accounts or overload services.
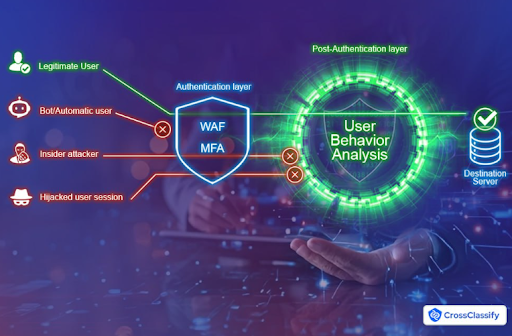
MFA and WAF Are Not Enough in Healthcare Cybersecurity
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and web application firewalls (WAF) are useful but insufficient in healthcare environments. Sophisticated attackers bypass MFA through SIM swapping, phishing kits, or malware. WAFs fail to detect behavioral anomalies, internal misuse, or device-level inconsistencies. As discussed in this article, true security requires adaptive and context-aware systems that go beyond perimeter defenses.
How CrossClassify Helps Protect Healthcare Organizations
•
Continuous Monitoring in Clinical Networks: Continuously tracks user behavior across EMRs, telemedicine portals, and patient apps. It spots anomalies in session length, click patterns, and device usage. Learn about CARTA•
Behavior Analysis for Medical Staff and Patients: Identifies unusual login behaviors, suspicious click sequences, or inconsistent typing speeds to flag fraudulent access. Explore behavioral biometrics•
Geo Analysis in Remote Care: Detects access attempts from unexpected geographies or multiple locations in short time frames, common in account takeovers. Understand device fingerprinting•
Link Analysis in Healthcare Fraud Rings: Maps connections between accounts, devices, and actions to uncover collusion or shared infrastructure among fraudsters. Learn about fraud detection•
Enhanced Security and Accuracy for Claims Systems: Combines risk scoring with identity verification to reduce false positives and block high-risk actions. Explore fraud risk management•
Seamless Integration into Health IT Ecosystems: Easily connects to EHR systems, appointment tools, and patient apps without disrupting workflows. See how integration works•
Alerting and Notification for Critical Events: Real-time notifications enable security teams to act instantly on suspicious activity, whether it's a credential leak, session hijack, or unverified device login.
Conclusion
The healthcare industry faces a unique and growing challenge in managing fraud and cybersecurity threats. From billing fraud and insider misuse to advanced bot attacks and account takeovers, the threats are as diverse as they are dangerous. Compliance with HIPAA and other regulations is necessary, but no longer sufficient. Organizations must shift from passive defense to active threat detection and response using intelligent, adaptive technologies.
CrossClassify empowers healthcare providers, insurers, and app developers with AI-driven fraud detection, device fingerprinting, behavior analytics, and risk-based alerts. Its solutions are tailored for healthcare workflows and integrate easily with existing platforms. With CrossClassify, healthcare organizations can protect patient data, detect fraud in real-time, and stay compliant in an ever-evolving digital environment.
Explore CrossClassify today
Detect and prevent fraud in real time
Protect your accounts with AI-driven security
Try CrossClassify for FREE—3 months
Share in
Frequently asked questions
The most common types include billing fraud in healthcare claims, insider data abuse, and account takeovers of staff or patients. CrossClassify detects these risks using behavior analytics, device fingerprinting, and real-time risk scoring. Learn more about fraud risk management
Account takeover protection in healthcare systems is vital as attackers target patient portals, telemedicine apps, and admin dashboards using phishing or stolen credentials. CrossClassify protects against this with session-based behavior analysis and device fingerprinting. See how it works
Yes, insider threat detection in healthcare organizations is a growing priority as staff can accidentally or maliciously leak data. CrossClassify identifies unusual access patterns and flags behavior anomalies across clinical systems. Explore more about insider threats
Telemedicine fraud detection software is now essential as fake consultations, ID theft, and device spoofing are becoming common. CrossClassify monitors user behavior and validates device integrity to block suspicious sessions. See techniques
Synthetic identity fraud in healthcare apps involves mixing real and fake data to bypass KYC. CrossClassify detects synthetic profiles using fingerprinting, geo anomalies, and behavioral scoring across sessions. Learn how to catch them
No, MFA is not enough for HIPAA-compliant healthcare platforms as attackers can bypass it via SIM swapping or session hijacking. CrossClassify strengthens security using adaptive analytics, risk context, and fraud fingerprints. Learn more
Bot protection in healthcare login systems is critical since bots can test stolen passwords, scrape data, or overload portals. CrossClassify stops bots with anomaly detection and human-device interaction profiling. Learn how
AI fraud detection for healthcare claims processing can stop fake billing, collusion, and upcoding. CrossClassify adds identity verification, link analysis, and scoring to claims workflows to flag anomalies. Explore use cases
Real-time monitoring for patient data protection enables detection of policy violations, device compromise, and insider abuse before damage occurs. CrossClassify offers 24/7 behavioral and device-based tracking across all endpoints. Learn more
Accurate fraud detection in healthcare systems is difficult without intelligent scoring. CrossClassify reduces noise by combining behavioral biometrics, device risk, and context to deliver precise threat decisions. Read how
Let's Get Started
Discover how to secure your app against fraud using CrossClassify
No credit card required
